Top 10 Alternative Energy Sources You Should Know About in 2023
As the world faces the escalating consequences of climate change and fossil fuel depletion, the importance of exploring and utilizing Alternative Energy Sources has never been more critical. In 2023, there is a growing recognition of the need for cleaner, sustainable energy solutions that can effectively meet our increasing energy demands while minimizing environmental impacts. This shift towards renewable energy is not just a trend but a necessity for ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
In this context, various Alternative Energy Sources have emerged, showcasing their potential to reshape our energy landscape. From solar and wind power to the innovative advancements in bioenergy and geothermal energy, the variety of options available provides the opportunity to cultivate a more resilient energy infrastructure. These energy sources not only reduce our carbon footprint but also promote energy independence, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth. As we delve into the top 10 Alternative Energy Sources, it becomes clear that embracing these innovations is essential for both ecological preservation and energy security in an increasingly uncertain world.

Overview of Alternative Energy Sources
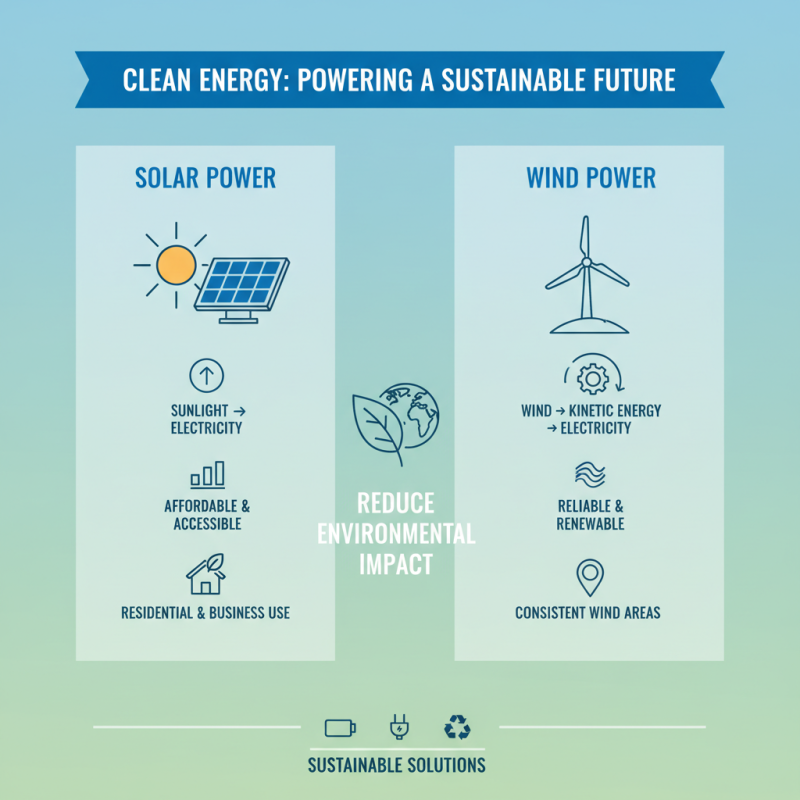
Alternative energy sources have gained significant attention as the world seeks sustainable solutions to meet its energy demands while reducing environmental impact. Solar energy, harnessed through photovoltaic cells, converts sunlight directly into electricity. This plentiful resource is increasingly affordable and accessible, allowing both individuals and businesses to generate clean power. Wind energy also plays a pivotal role, utilizing wind turbines to convert kinetic energy from wind into electricity, providing a reliable and renewable source of power, particularly in areas with consistent wind currents.
Another promising alternative is geothermal energy, which taps into the Earth's internal heat for electricity generation and direct heating applications. This method is particularly useful in regions with volcanic activity, where hot water and steam can be harnessed efficiently. Biomass, derived from organic materials, transforms waste into energy, serving as a versatile resource that can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, hydropower, generated from flowing water, continues to be a significant contributor to the energy mix, with its capacity to deliver consistent energy while providing additional benefits like flood management and irrigation support. Collectively, these alternative energy sources represent a crucial step toward a sustainable future, demonstrating the potential to power our lives while preserving the planet.
Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
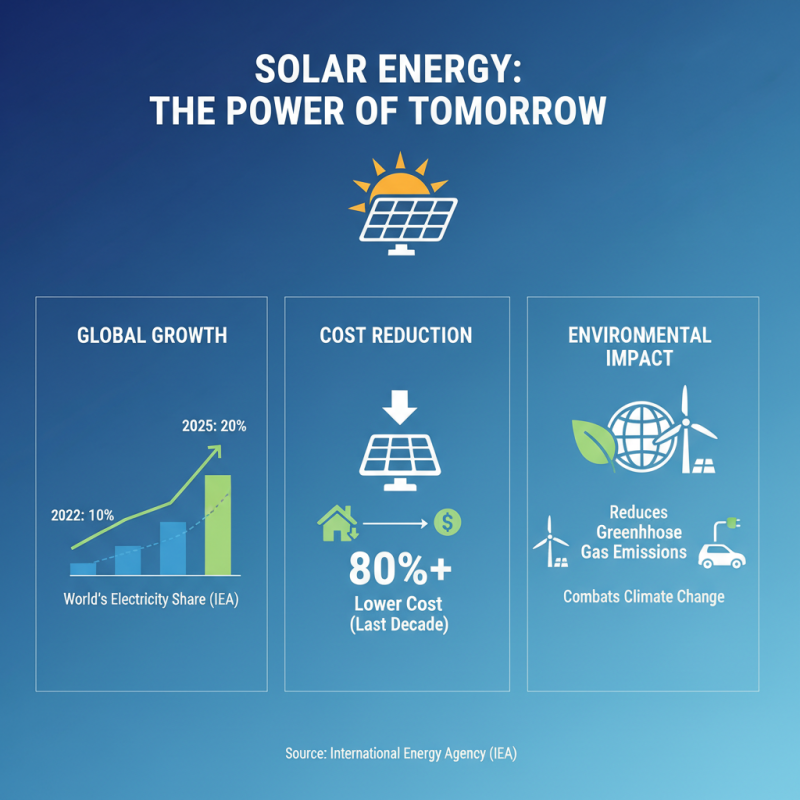
Solar energy is rapidly emerging as a primary alternative energy source, offering a sustainable and clean way to power our homes and industries. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar power accounted for nearly 10% of the world's electricity generation in 2022 and is projected to reach 20% by 2025, underscoring its importance in the global energy landscape. The advancements in photovoltaic technology have lowered the cost of solar panels by over 80% in the past decade, making solar energy more accessible than ever. This trend not only contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also plays a vital role in combating climate change.
Tips: When considering solar energy for your home, assess your roof's orientation and shading. South-facing roofs that receive ample sunlight throughout the day are ideal for solar panel installation. Additionally, homeowners can take advantage of local and federal incentives that can significantly reduce installation costs while increasing the return on investment.
As we look toward a future powered by renewable energy, solar energy remains at the forefront. The U.S. Department of Energy indicates that solar capacity is expected to grow by more than 160 gigawatts by 2024, spurred on by both residential and commercial adoption. This growth not only supports energy independence but also paves the way for job creation in the green technology sector, highlighting the multifaceted benefits of investing in solar power.
Tips: Regular maintenance of solar panels, such as cleaning and inspection, can improve efficiency and extend the lifespan of your system. Monitoring your energy output can also help you maximize savings and energy production.
Wind Energy: Capturing Nature's Breezes
Wind energy harnesses the natural currents of air to generate electricity, making it a potent and sustainable alternative energy source. As technology advances, wind turbines are becoming more efficient and capable of producing power even at lower wind speeds. This means that areas previously considered unsuitable for wind farms are now viable locations for harnessing wind energy. With its minimal environmental impact and ability to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, wind energy is paving the way for cleaner energy production as we move into 2023.
Tips for maximizing the adoption of wind energy include considering the local wind patterns before installation. Understanding the seasonal and daily wind trends can help in selecting the most effective turbine placement. Additionally, engaging with local communities can foster support for wind projects, addressing concerns and promoting awareness of the benefits of wind energy. Lastly, investing in the latest technology can increase efficiency and reduce maintenance costs over time, ensuring a more successful transition to renewable energy sources.
As we embrace wind energy, it's essential to explore innovative solutions such as community wind projects, which can empower local residents and promote sustainable practices. Encouraging individuals and businesses to invest in small-scale wind systems can contribute significantly to decentralized energy production and resilience in energy supply. By prioritizing education and awareness around wind energy, we can increase its adoption and create a more sustainable future for all.
Top 10 Alternative Energy Sources You Should Know About in 2023
Wind Energy: Capturing Nature's Breezes
Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy, harnessed from the Earth’s internal heat, is quickly becoming a prominent player in the alternative energy landscape. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), geothermal energy has the potential to provide approximately 200 gigawatts (GW) of generating capacity globally by 2050, contributing significantly to the world's energy needs. The unique advantage of geothermal power lies in its reliability; it delivers a steady energy supply, unlike other renewable resources that are contingent on weather conditions. In regions with suitable geological formations, geothermal energy can enable continuous, baseload power generation, making it a stable choice for energy grids.
The utilization of geothermal energy goes beyond electricity generation; it also plays a critical role in direct heating applications. The Geothermal Energy Association (GEA) reports that in 2021, direct-use applications contributed to around 30 billion megawatt-hours (MWh) of energy in the U.S. alone, which is a testament to its versatility. From heating buildings to supporting agricultural practices through greenhouse heating, the benefits are broad-reaching. With advancements in technology, enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are being explored, which could expand the geographical range where geothermal energy can be effectively harnessed. This evolution positions geothermal energy as not only a key player in the transition towards sustainable energy solutions but also a critical asset in combatting climate change, with a minimal carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
Bioenergy: Renewable Resources from Organic Materials
Bioenergy, derived from organic materials, represents a significant part of the alternative energy landscape in 2023. This renewable resource has gained traction due to its potential to utilize waste materials, such as agricultural residues, forestry by-products, and even municipal solid waste, to produce energy. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), bioenergy accounted for approximately 10% of global energy supply in 2020, making it one of the largest sources of renewable energy. With advancements in technology, the efficiency of converting biomass into energy has improved, allowing for more sustainable practices and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The growth of bioenergy is bolstered by its versatility; it can be converted into electricity, heat, or biofuels for transportation. A report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) projects that the potential for bioenergy consumption could rise significantly, with estimates indicating an increase in biomass sources by over 40% by 2035. This shift promises not only to support energy security but also to contribute to rural economic development, as it creates job opportunities in biomass production and processing. Furthermore, the expansion of bioenergy aligns with global goals aimed at achieving climate neutrality, highlighting its crucial role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
| Energy Source | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bioenergy | Energy produced from organic materials, including plants, agricultural and forestry residues, and waste. | Renewable, can help reduce waste, can provide a stable energy source. | Land use changes, potential competition with food production, emissions if not managed properly. | Contributes to energy security, reduces greenhouse gases, supports rural economies. |
| Solar Energy | Energy harnessed from sunlight using solar panels and other technologies. | Abundant and sustainable, low operational costs after installation. | High initial costs, weather dependent, space requirements for large installations. | Reduction in reliance on fossil fuels, positive environmental impact. |
| Wind Energy | Energy generated from air flow using wind turbines. | Clean energy source, low operational costs, creates jobs. | Intermittent energy source, potential impact on wildlife, noise pollution. | Supports grid stability, reduces carbon emissions. |
| Hydropower | Energy produced from moving water, typically using dams. | Reliable, can provide large amounts of electricity, flexible in power generation. | Environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems, displacement of communities. | Provides baseload power, contributes to grid stability. |
| Geothermal Energy | Energy harnessed from the heat stored beneath the Earth's surface. | Sustainable and reliable, low emissions. | Limited to certain geographical areas, potential for induced seismicity. | Can provide continuous energy supply, reduces dependence on fossil fuels. |
| Tidal Energy | Energy generated by harnessing the movement of tides. | Predictable energy source, low emissions. | High upfront costs, potential ecological disruption. | Contributes to energy diversity, enhances coastal energy resilience. |
| Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion | Energy derived from temperature differences in ocean water. | Renewable and abundant, can produce fresh water as a byproduct. | High technology costs, limited to warm ocean regions. | Innovative solution for energy and water scarcity. |
| Hydrogen | Energy carrier produced from the electrolysis of water or natural gas reforming. | Flexible uses in transportation and industry, emits only water when used in fuel cells. | Current production methods can be carbon-intensive, infrastructure challenges. | Potential to decarbonize heavy industries and transportation. |
| Waste-to-Energy | Energy produced by converting non-recyclable waste materials into usable forms of energy. | Reduces landfill waste, generates energy and recycles materials. | Potential emissions concerns, can be costly to implement. | Enhances waste management strategies, contributes to renewable energy goals. |
| Biogas | Natural gas produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. | Renewable and sustainable, reduces greenhouse gas emissions from landfills. | Variable production based on feedstock availability, requires management of byproducts. | Supports energy independence, enhances agricultural sustainability. |
Related Posts
-

Challenges Faced by Global Buyers Seeking the Best Green Energy Solutions
-

Exploring the Unique Features and Applications of the Best Sustainable Energy Products in Today's Market
-

10 Ways Renewable Energy Transforms Our Future
-

Leading Hybrid Solar Inverter Manufacturers from China at the 137th Canton Fair
-

The Ultimate Guide to Harnessing the Best Renewable Energy Options for Your Business
-

The Future of Gas Turbines: Innovative Technologies Shaping Sustainable Energy Solutions
